by Michael Leroy Oberg
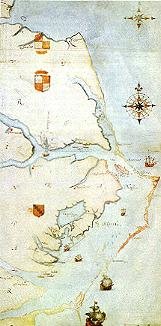
It was on the fourth of July in 1584 that Philip Amadas and Arthur Barlowe, soldiers and sailors both in the service of Sir Walter Ralegh, arrived off the coast of what is today North Carolina, setting in motion the forces that would transform the life of Manteo The two explorers travelled with instructions to scout out the location for the colony Ralegh hoped to establish in America in the very near future.
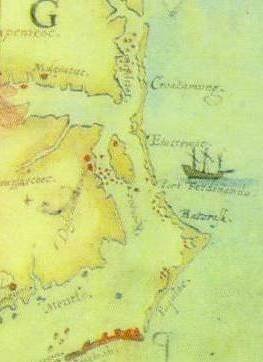
By the 13th ofJuly, the English voyagers had landed on Hatorask Island, taking possession of the land in the name of the Queen 'according to the ceremonies used in such enterprises'. They then returned to their two ships, anchored off the western side of the island, and waited. On the third day, according to Barlowe, they 'espied one small boate rowing towards us, having in it three persons'. These Roanoke Indians landed at Hatorask. Two of them remained with their boat while 'the third came along the shoare side towards us'. Where 'he walked up and downe upon the point of the lande next unto us'. Several Englishmen, including Barlowe and Amadas, rowed ashore to greet him. After the lone Indian 'had spoken of many things not understoode by us, we brought him with his owne good liking, aboord the shippes, and gave him a shirt, a hatte, and some other things, and made him taste of our wine, and our meate, which he liked very well'. He then 'requited the former benefits receaved' before he departed by providing the explorers with enough fish for an impressive banquet.
The three natives returned to Roanoke Island with word that the newcomers posed no threat, for the next day, Barlowe reported, 'there came unto us divers boats, and in one of them the Kings brother, accompanied with fourtie or fiftie men, very handsome, and goodly people, and in their behaviour as mannerly, and civill, as any of Europe'. Granganimeo, the brother of the Roanoke weroance Wingina, met the English on the shore, and 'made all signes of joy, and welcome, striking on his head, and his breast, and afterwardes on ours, to shewe we were all one, smiling and making shewe the best he could, of all love, and familiaritie'.
'We were all one', Granganimeo tried to tell Barlowe. The Roanokes took great interest in the English voyagers. Trading commenced quickly. Indians offered deerskins for English trade goods. Others brought 'with them leather, corrall, divers kindes of dies very excellent, and exchanged with us'. Such intercultural exchange provided the foundation for a fragile middle ground on the coast of Hatorask Island, as Indians and Englishmen each took steps to incorporate the other into their own conceptual world, and to make sense of the strangers they then were encountering.
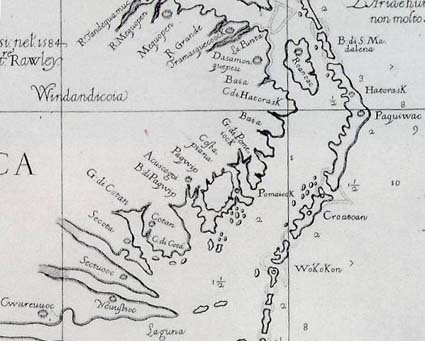
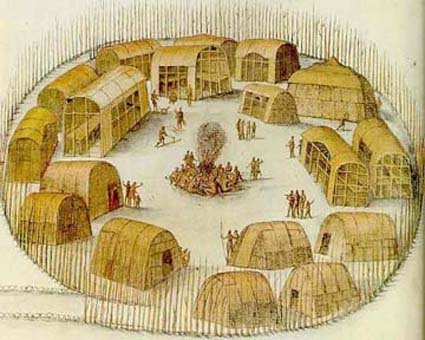
After several days, and after the Indians 'had beene divers times aboord our shippes', Barlowe and seven others sailed around the southern tip of Roanoke Island, and north along the island's western shore, before stopping for several nights at the Roanokes' village 'of nine houses, built of Cedar, and fortified round about with sharpe trees, to keepe out their enemies', on the northern tip of the island. Though far from trusting entirely in his hosts, Barlowe wrote that he and his companions 'were entertained with all love, and kindness and with as much bounties after their manner, as they could possibly devise'.
What Barlowe saw on Roanoke Island impressed him. The Indians were pure of heart, he wrote, and friendly. 'Wee found the people most gentle, loving, and faithful, void of all guile, and treason, and such as lived after the manner of the golden age. The earth', he wrote, brought forth for the Indians 'all things in aboundance, as in the first creation, without toile or labour'. Roanoke, or the surrounding islands, Barlowe reported, would provide the ideal location for a future English settlement.